A new methodology to detect corrosion on steel truss railway bridges exploiting local strain gauges: Analytical, numerical, and experimental validation.
Authors:
Abstract:
Steel truss bridges suffer from ageing deterioration phenomena, among which corrosion is the most critical. Several works in the literature proved strain gauges effective in assessing corrosion effects over bridge truss elements. This paper proposes a novel diagnostic methodology based on measurements performed by resistive micro-strain gauges applied to end diagonals and midspan lower chords of a Warren truss bridge. Data were collected from a permanent monitoring system in normal operating conditions. The authors introduce a new damage-sensitive feature (DSF), independent from operational variables, to enhance performance of corrosion damage detection. The proposed index consists of the normalised area of the strain time series recorded on instrumented bridge members. The proposed DSF is robust to noise and independent of train characteristics (speed, weight, number of axles, etc.). The normalisation is realised by exploiting some strain gauges on the track segment, whose records are processed to extract train axle load, speed, and spacing according to a weigh-in-motion (WIM) algorithm herein described. Starting from the DSF, a damage-extent index (DEI) is defined, which allows damage quantification. The methodology is based on an analytical derivation, supported by numerical outcomes and tested, also, on experimental data. A calibrated bridge 3D FE model, on which local corrosion scenarios are simulated, is employed. Tests on a 3 months experimental dataset demonstrate the DSF robustness to operational parameters, with a coefficient of variation below 2.5%, as well as the DEI effectiveness, that maintained a zero average value, in accordance with the condition of a healthy bridge.

Featured papers
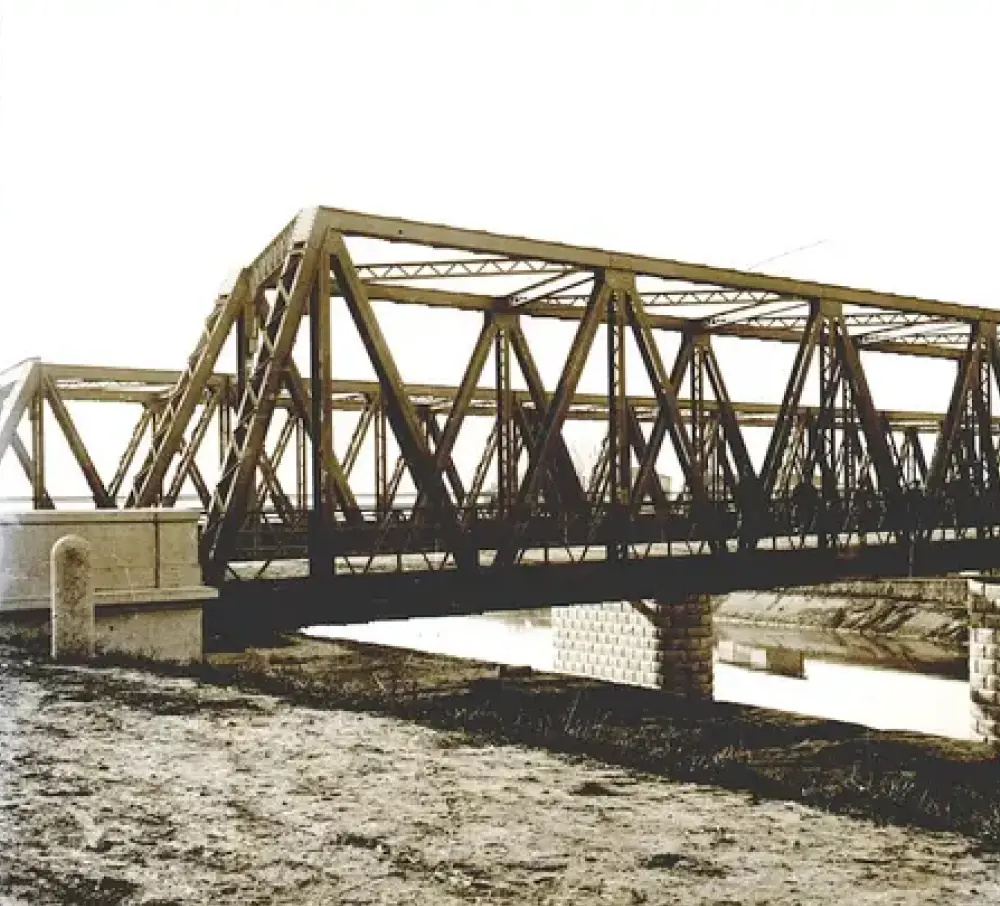

An automated algorithm for experimental OMA: application on a Warren truss railway bridge with a permanent monitoring system
In the attempt to move towards time-efficient and cost-effective condi-tion-based monitoring of transport infrastructures...
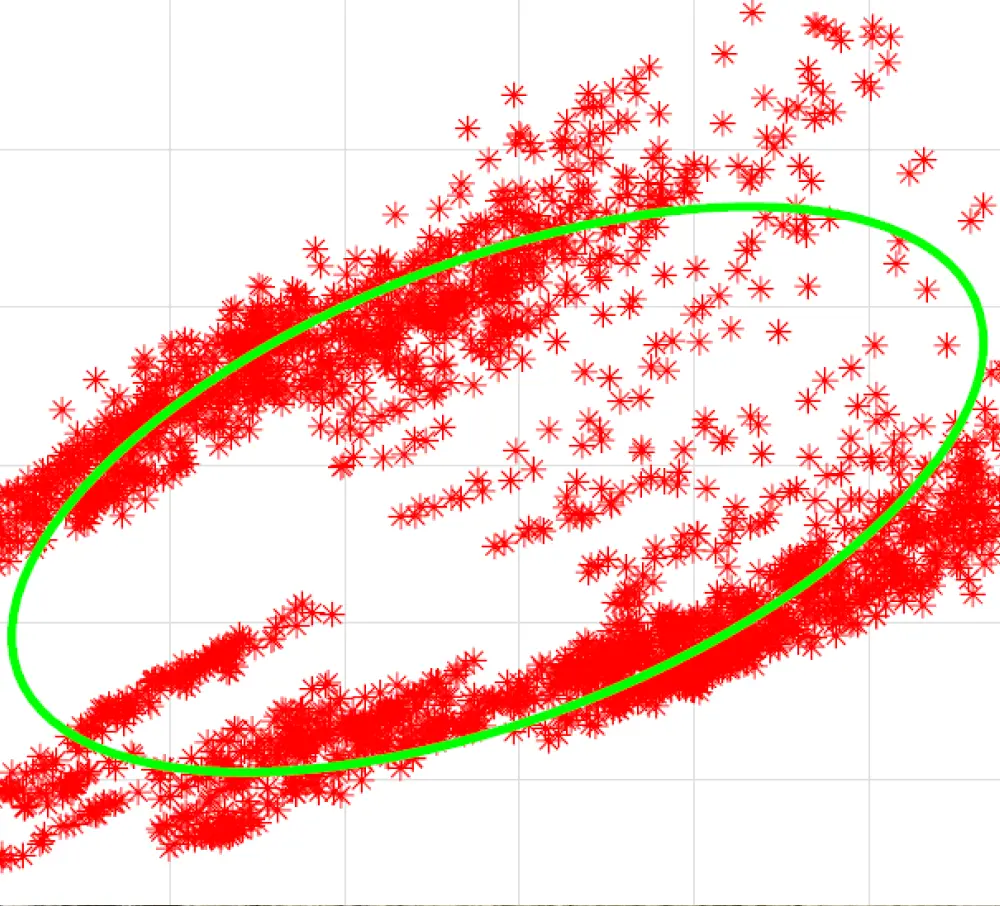
Improving the effectiveness of anomaly detection in bridges through a deep learning method based on coherence of signals
In recent years, real-time monitoring of health conditions for massive structures, such as bridges and buildings, has grown in interest...
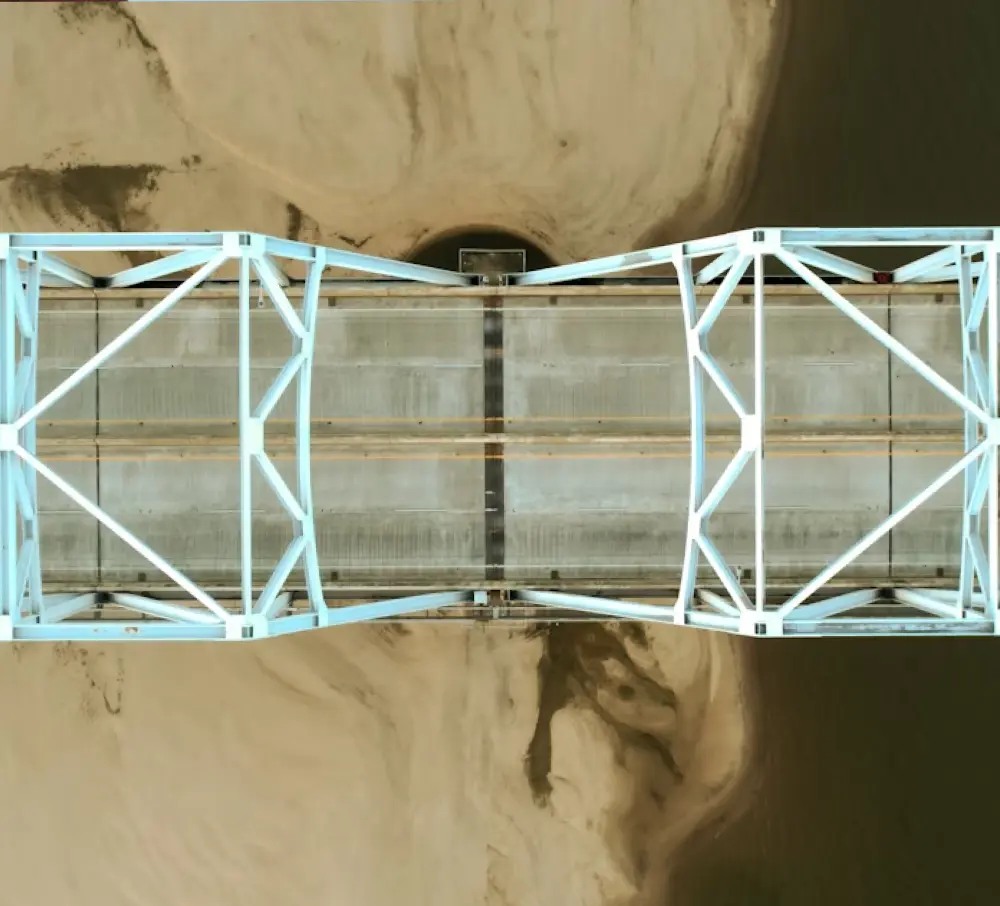

On the performance of data‑driven dynamic models for temperature compensation on bridge monitoring data
In Structural Health Monitoring, environmental and operational variables present a persistent challenge...
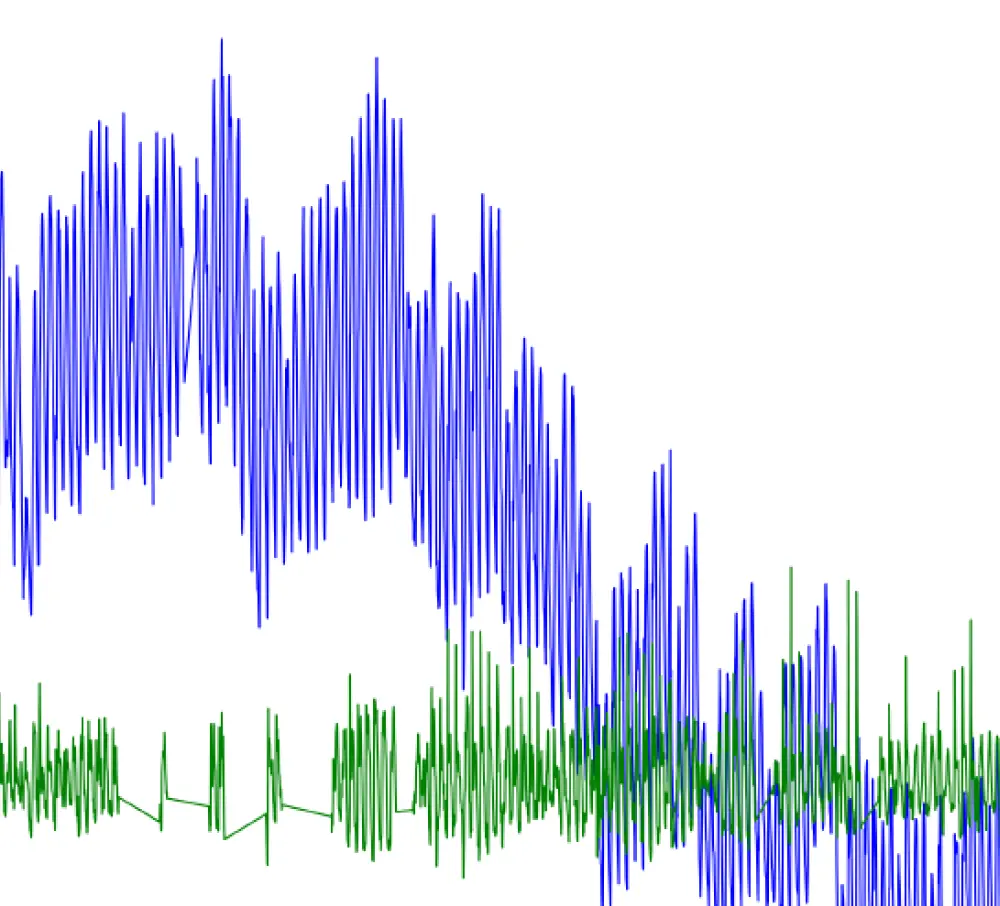
Design and Application of a Statistical Learning Methodology to Remove Temperature Effect on Static Signals for Bridge Structural Health Monitoring
Infrastructures are essential for the development and flourishing of countries; in this context, bridges play an irreplaceable role as links for goods and people...